Best purchase I’ve made this winter! The color and knitting are exquisite and it’s so comfy! Went from NYC to Miami without ever taking it off. Super cute!!
- Email: sales01@hongjienterprise.com
- Tel: +86 15605507266

Best purchase I’ve made this winter! The color and knitting are exquisite and it’s so comfy! Went from NYC to Miami without ever taking it off. Super cute!!
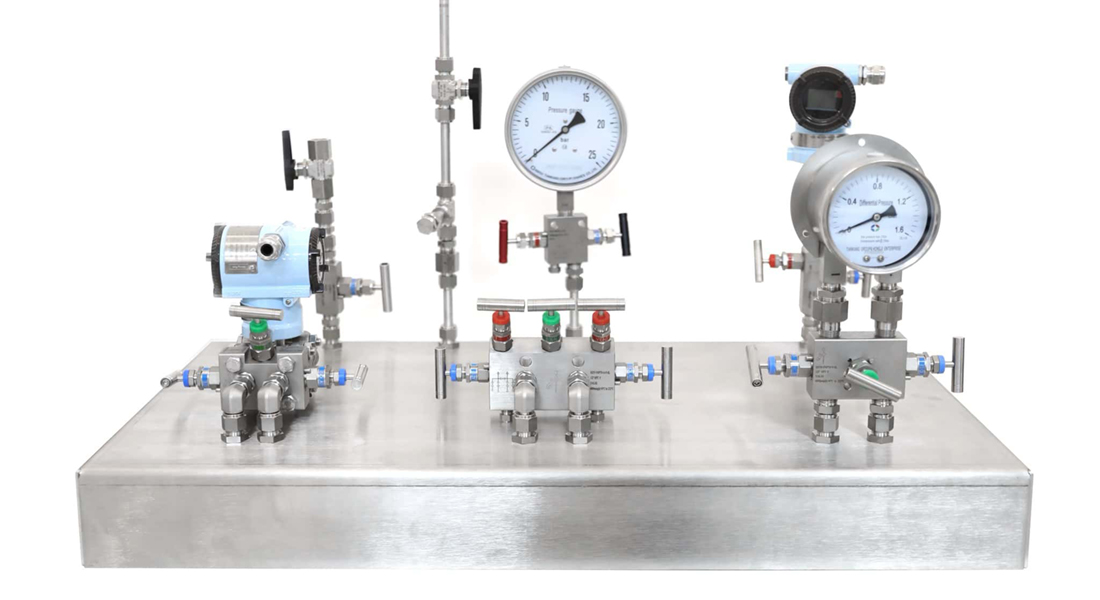
Anhui Hongji gauge valve manifolds and transmitter valve manifolds are essential accessories commonly used in industrial pipeline and instrumentation systems. Although similar in structure, they have slightly different functions and applications.
Ⅰ. Gauge Valve Manifolds
Gauge valve manifolds (commonly known as gauge needle valves or valve sets) are typically installed between a pressure gauge and the pipeline. Their primary functions include:
1.Isolation and Shut-off:
2.Vent, Drain, and Blow-down:
3.Pressure Gauge Protection:
4.Calibration and Testing:
Typical Structure:
Ⅱ. Pressure Transmitter Valve Manifolds
Transmitter valve manifolds (typically called 3-valve or 5-valve manifolds) are usually installed between a pressure transmitter and the pipeline. Their main functions include:
1.Isolation and Transmitter Protection:
2.Pressure Equalization and Calibration:
3.Venting, Draining, and Air Bleeding:
4.Improved Measurement Accuracy and Reliability:
Typical Structure:
III. Summary of Differences
| Features | Gauge Valve Manifold | Transmitter Valve Manifolds |
| Primary Applications | Isolation, venting, gauge protection | Isolation, equalization,calibration, transmitter protection |
| Typical Structure | Single/Double/Triple valve arrangement | 3-valve or 5-valve arrangements |
| Typical Scenarios | Single-point pressure measurement | Differential pressure, liquid level, flow, and pressure measurement |
| Accuracy Requirements | General accuracy | Higher accuracy |
Ⅳ. Applications:
Gauge Valve Manifold Example:
Installed on a boiler pipeline, the manifold allows quick isolation of the pressure gauge during maintenance or replacement without interrupting system operation.
Transmitter Valve Manifold Example:
Used with differential pressure transmitters in flow measurement systems (such as orifice plates), a 5-valve manifold enables online calibration and easy maintenance without impacting production.
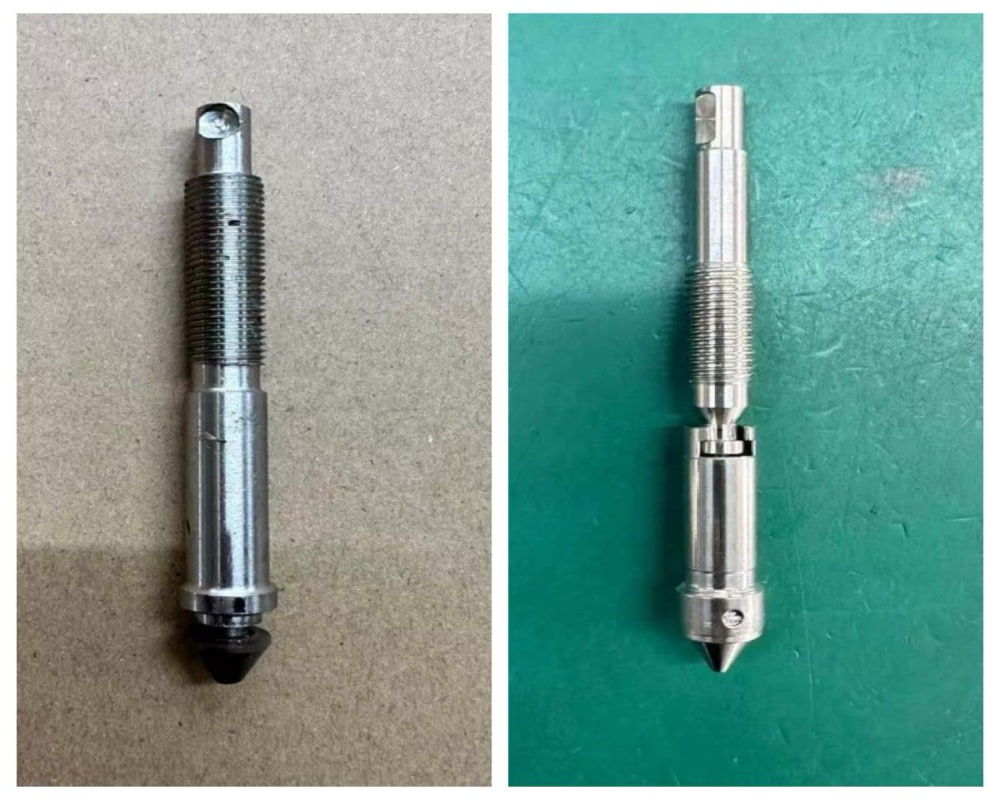

What is the difference between Valvento instrumentation Valve manifold and other brands.
Stem DesignInstead of using integral stem, we are using two split joint stem ro realize the lower stem is non-rotating function, in this way, it could minimize the abrasion between the tip and seat, extend the life cycle.
No only that, we also involve special chemcial treatment to harden the stem to make it more endurence under high torque. Stellite tip and Ceramic tip also available for option, locked pin design on lock nut to proevent unexpected loosen, also the grinding process involved on body surface to remove visible defects with the naked eye. If you have any needs for the valve manifolds pls feel free to contact us!
Leave A Message